Unveiling the Simplicity of Half Wave Rectification in Multisim
In the vast landscape of electronics, where currents flow and signals dance, there exists a fundamental building block that shapes the very essence of modern technology: the rectifier. Like a gatekeeper, it selectively allows the passage of electrical current, transforming alternating current (AC) into the direct current (DC) that powers our devices. Among these rectifiers, the half wave rectifier stands as a testament to elegant simplicity.
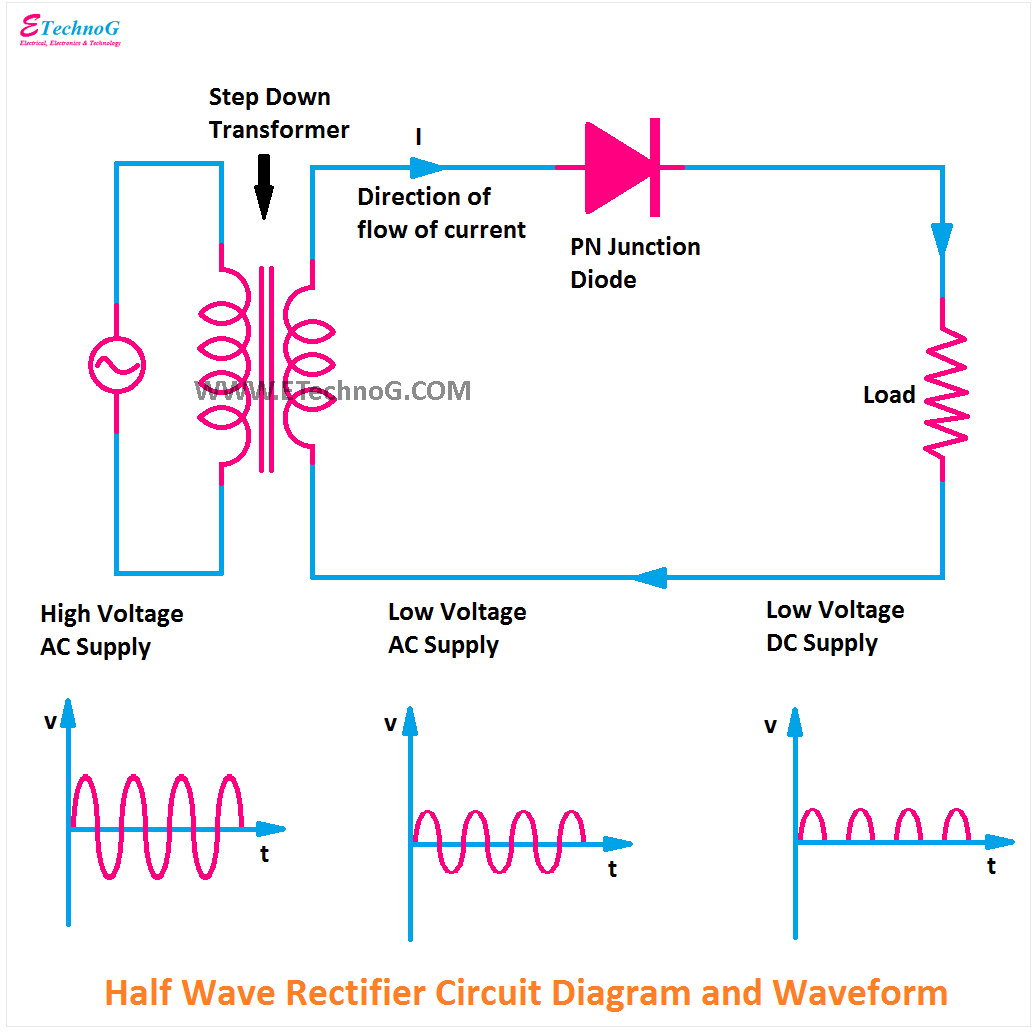
Imagine a single diode, acting as a one-way valve for electricity. This is the heart of a half wave rectifier circuit. When the AC signal's positive half-cycle arrives, the diode opens, allowing current to flow through. During the negative half-cycle, the diode closes, effectively blocking the current. This pulsating DC output, while not perfectly smooth, is the first step in converting AC to usable DC.
Multisim, a powerful circuit simulation software, provides a virtual playground to explore and understand these fundamental concepts. Creating a half wave rectifier circuit diagram in Multisim is akin to building it in the real world, but with the added advantage of risk-free experimentation. One can visualize the current flow, measure voltages, and tweak component values with ease, gaining valuable insights into the rectifier's behavior.
The historical roots of rectification can be traced back to the early days of radio, where the need to convert AC signals into DC for powering vacuum tubes became crucial. The half wave rectifier, in its simplicity, emerged as a foundational solution. Its importance continues to this day, forming the basis of more complex rectifier circuits and playing a vital role in power supplies, signal processing, and various electronic applications.
One of the primary challenges associated with half wave rectification is the inherent ripple in the output DC voltage. This pulsating nature can be undesirable for sensitive electronic components, necessitating further filtering stages to smooth out the voltage. However, the simplicity and cost-effectiveness of the half wave rectifier often outweigh this drawback in less demanding applications.
A simple example of a half wave rectifier circuit comprises an AC voltage source, a diode, and a resistor representing the load. The AC source provides the input signal, the diode performs the rectification, and the resistor simulates the circuit or device consuming the rectified DC power. Observing the voltage across the resistor in Multisim reveals the pulsating DC output waveform.
Three key benefits of using Multisim for simulating half wave rectifier circuits are: visualization of circuit behavior, risk-free experimentation, and efficient troubleshooting. Visualizing current flow and voltage levels helps solidify understanding. The virtual environment allows for component changes and parameter adjustments without the risk of damaging physical components. Troubleshooting becomes easier with built-in measurement tools and analysis capabilities.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Half Wave Rectifier
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Simple circuit design | Low efficiency due to utilization of only half of the input AC wave |
| Low cost due to fewer components | High ripple content in the output DC voltage |
| Easy to implement | DC output voltage is lower than the peak AC input voltage |
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. What is a half wave rectifier? A: A circuit that converts AC to pulsating DC by allowing only one half of the AC cycle to pass.
2. Why use Multisim? A: Multisim allows for virtual circuit building and testing, facilitating learning and experimentation.
3. What is the main disadvantage? A: The significant ripple in the output DC voltage.
4. What is a diode? A: A semiconductor device acting like a one-way valve for electricity.
5. What are the applications? A: Power supplies, signal processing, and other electronic applications.
6. How can ripple be reduced? A: By using filtering circuits like capacitors.
7. Why is DC important? A: Many electronic devices require DC for operation.
8. How to simulate in Multisim? A: Place components, connect them, and run the simulation.
In conclusion, the half wave rectifier circuit, while simple in design, plays a fundamental role in electronics. From its historical origins in early radio to its continued relevance in modern applications, its ability to convert AC to DC remains crucial. Multisim empowers learners and engineers to explore the nuances of this circuit, visualize its behavior, and understand its limitations. Embracing the power of simulation opens doors to innovation and deeper comprehension of this essential building block of electronic circuits. By understanding the principles of half wave rectification, we gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate workings of the technology that surrounds us, encouraging us to further explore the fascinating world of electronics. Begin your journey of discovery today by experimenting with a half wave rectifier circuit in Multisim.
The delicate dance of fleur de sel a culinary treasure
Finding comfort in scripture when moving away
Mastering electronic symbols your guide to circuit diagrams